How is Blockchain Technology Changing the Metals & Mining Industry?
As the world transitions from fossil fuels to green energy, massive growth opportunities exist for the mining and metals industry, specifically in the Americas. However, corruption, environmental destruction, and human rights abuse plague the mining world. Swapping out carbon-intensive energy with green energy powered by ‘dirty’ metals hardly feels like a solution. To comply with the growing demand from overseeing governing bodies, traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain are essential. Blockchain technology provides a unique solution for the mining and metals industry.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. An asset can be tangible (metals, cash, land) or intangible (digital certifications, intellectual property, patents, copyrights). Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network, reducing risk, cutting costs, and allowing for full traceability.
How can blockchain be integrated into the Green Metals Supply Chain?
Due to increased regulatory pressures and a shift in ESG-led investment, downstream manufacturing companies such as electronics, automotive companies, and green energy producers are increasingly demanding the following traceability from upstream producers with regards to the metals and minerals in their end products:
1. Provenance: What is the metal ore source of origin? From which mines/miners are the minerals and metals in their end products?
2. Production methods: Under which processes are they produced? Are they produced responsibly & sustainably?
Critical minerals producers such as Alquimista have built their business models around these solutions to provide greater assurance for social and environmental standards. In the minerals and metals supply chain, the following properties of minerals could be recorded onto a blockchain system:
Weight
Quantity
Grade
3D images of the material
Mineral fingerprints
Ownership of the material at a specific supply chain point
Life cycle assessments
Bills of lading
Transfer locations
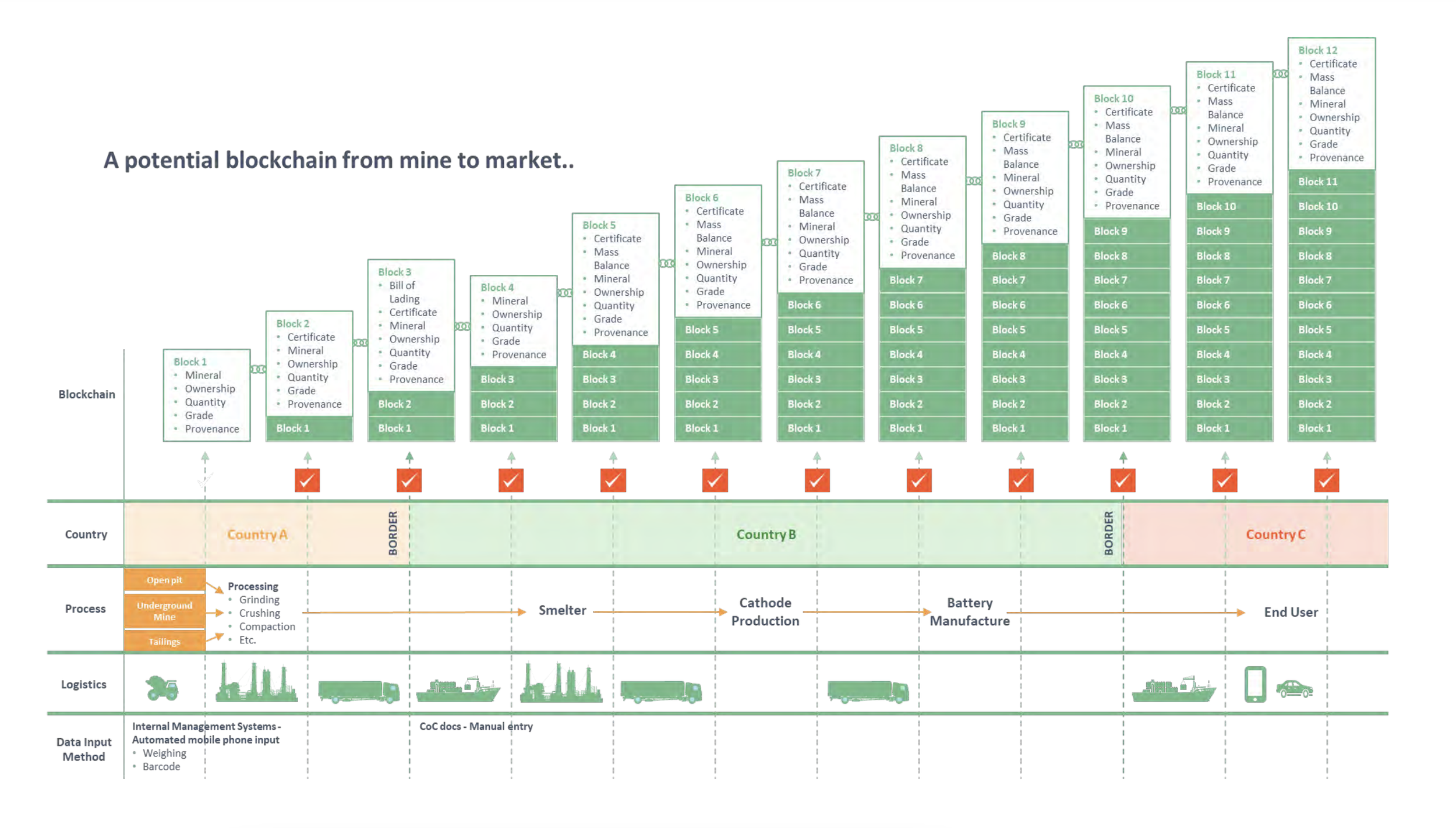
Tracking the data through the supply chain from upstream to downstream producers would allow a secure Chain-of-Custody (CoC) to be established. Below is a potential blockchain from mine to market.
Source: RCS Global, 2017
What benefits does integrating Blockchain technology have in the Metals & Mining supply chain?
Investment in the critical metals supply chain is challenging due to strict regulations and restrictions aimed at reducing the impact on climate change and human rights abuse. For example, in the U.S., receiving approval for a new mining project can take seven to 10 years. While many factors play into the lengthy approval process, complying with rigorous environmental standards plays a prominent role. Blockchain technology may help reduce timelines, costs, and risk because of the following advantages:
Blockchain builds a consensus and trust around responsible & sustainable production standards between downstream and upstream companies.
The immutability of decentralized control over a blockchain system minimizes the risk of fraud.
Defined datasets and digital certificates can be made accessible to downstream buyers, auditors, investors, etc., in real-time while remaining encrypted to share proof of fact rather than confidential information, trade secrets, or protected intellectual property.
A blockchain network can be scaled to include other producers and supply chains beyond those initially involved.
Cost reduction due to the paperless nature of a blockchain-enabled CoC system, the potential decrease in audits, and the reduction in transaction costs
Thus, blockchain technology allows governments and corporations to minimize costs, reduce risk, and compete in the global green energy market while reducing carbon emissions and overcoming traceability barriers.